Abstract
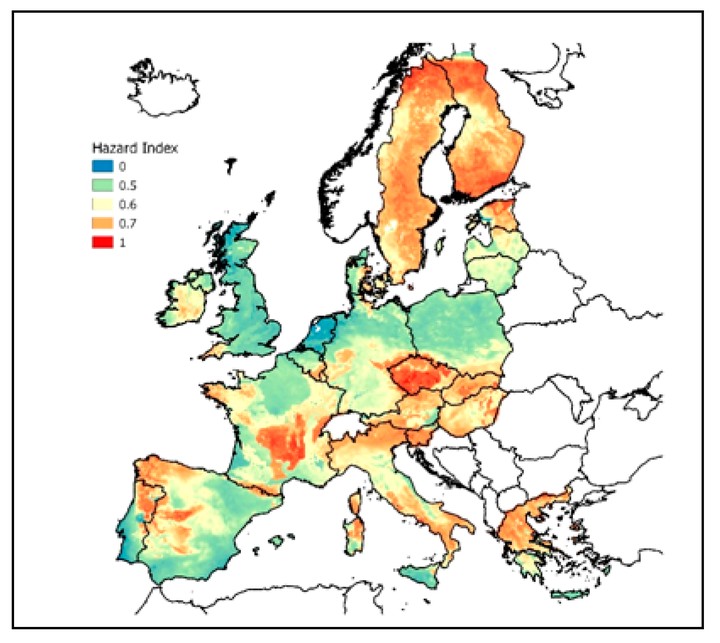
Exposure to indoor radon at home and in workplaces constitutes a serious public health risk and is the second most prevalent cause of lung cancer after tobacco smoking. Indoor radon concentration is to a large extent controlled by so-called geogenic radon, which is radon generated in the ground. While indoor radon has been mapped in many parts of Europe, this is not the case for its geogenic control, which has been surveyed exhaustively in only a few countries or regions. Since geogenic radon is an important predictor of indoor radon, knowing the local potential of geogenic radon can assist radon mitigation policy in allocating resources and tuning regulations to focus on where it needs to be prioritized. The contribution of geogenic to indoor radon can be quantified in different ways: the geogenic radon potential (GRP) and the geogenic radon hazard index (GRHI). Both are constructed from geogenic quantities, with their differences tending to be, but not always, their type of geographical support and optimality as indoor radon predictors. An important feature of the GRHI is consistency across borders between regions with different data availability and Rn survey policies, which has so far impeded the creation of a European map of geogenic radon. The GRHI can be understood as a generalization or extension of the GRP. In this paper, the concepts of GRP and GRHI are discussed and a review of previous GRHI approaches is presented, including methods of GRHI estimation and some preliminary results. A methodology to create GRHI maps that cover most of Europe appears at hand and appropriate; however, further fine tuning and validation remains on the agenda.